4.1.9 Drupal CMS Installation

Drupal is a free content management system (CMS, Content Management System) with open source code, built for complex and flexible web projects: corporate portals, government websites, news portals, and online communities.
It is written in PHP, uses MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQLite, and runs on any web server with PHP support — Apache, Nginx, or LiteSpeed.
Drupal is distinguished by a modular architecture and scalability:
- the core can be extended with thousands of modules from the official repository;
- supports complex data structures and user roles;
- includes the Twig templating system;
- allows you to create REST and JSON:API interfaces;
- optimized for SEO, caching, and security.
In essence, Drupal is a framework-level builder that is suitable not only for content sites but also for high-load platforms with custom business logic.
Important! Regularly update Drupal CMS and installed modules. This is crucial for protection against vulnerabilities and compatibility with new versions of PHP and MySQL. Always back up your site and database before updating.
Server preparation
Requirements
Environment variables
DOMAIN_NAME— the site’s domain nameDB_NAME,DB_USER,DB_PASSWORD— database parametersDRUPAL_ROOT— Drupal installation directory
Installation Drupal on hosting
- Download the archive from the official Drupal website.
- Upload the archive to your domain folder (
~/www/DOMAIN_NAME) via FTP or the file manager in the hosting panel. - Create a database.
- Open your domain in the browser:
http://DOMAIN_NAME— the installer should start.
- Specify the language, database parameters, and admin credentials.
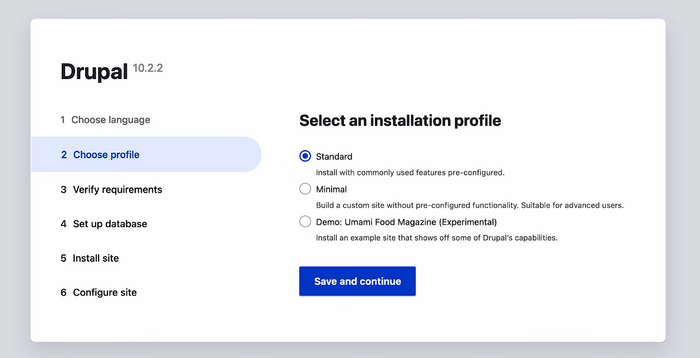
- After installation, delete the installer script (usually
core/install.php) or ensure it is inaccessible.
Configuring Drupal additional features
Configuration
The Drupal configuration file is located at:
- Hosting:
~/www/DOMAIN_NAME/sites/default/settings.php - VPS:
/var/www/DOMAIN_NAME/sites/default/settings.php
For more details, see our guide.
SSL certificate
For HTTPS, use Let’s Encrypt or a commercial SSL certificate
Performance optimization
- Enable caching (Drupal → “Configuration → Performance”)
- Install and enable the Redis or Memcache module for external caching
- Enable OPCache at the PHP level
- CSS/JS aggregation — combine and minify
Security
- Install the Security Review module — it will audit your configuration
- Restrict access to
settings.php,services.yml,composer.json, and other critical files - Configure Trusted Host Patterns (protection against HTTP Host Header attacks)
- Periodically update the core and modules via Composer or the internal update mechanism
Verification
- Go to
http(s)://DOMAIN_NAME/user/loginand log into the admin panel - In Reports → Status report check the system status
- Open the homepage and make sure it renders correctly
- Create a page (Content → Add content → Page) and check the display
- Ensure SSL works and HTTP redirects to HTTPS
Common errors
| Error / symptom | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| White screen (500) | Fatal PHP error or missing required extension | Enable error display and check logs; fix the root cause based on the error message |
| Failed to connect to DB | Incorrect DB_HOST/DB_USER/DB_PASSWORD, missing privileges, or DB/user not created |
Check host/DB name/login/password in ~/www/DOMAIN_NAME/sites/default/settings.php; create a user with access to the required DB |
No permissions for sites/default/files |
Insufficient permissions/ownership of the files directory | Set the web process owner and proper permissions: chown -R www-data:www-data sites/default/files · directories 755, files 644 (or group write where applicable) |
| Errors when updating modules | Updating via UI doesn’t pull in dependencies; outdated approach | Update via Composer: composer update drupal/<module> --with-dependencies or all packages; then drush updatedb and drush cache:rebuild |
Useful links
Official documentation