8.2.27 Mail-in-a-Box (MIAB): Install and Configure a Mail Server

Mail-in-a-Box (MAIB) is an automated mail stack installer. It deploys and integrates: Postfix (SMTP), Dovecot (IMAP/POP3), authoritative DNS and a recursive resolver (unbound), Nginx, Fail2ban, Roundcube, an admin panel with status checks, Let’s Encrypt, SPF/DKIM/DMARC policies, backups (local/S3/SSH) and Nextcloud (CalDAV/CardDAV, ActiveSync).
Advantages
- Removes manual assembly of MTA/IMAP/antispam/TLS.
- A single admin panel
/adminwith status checks and recommendations. - Built-in authoritative DNS eliminates manual record management at the registrar.
- Typical scenarios: corporate mail, test domains, isolation from SaaS.
Server preparation
Requirements
- Virtual or dedicated server.
- Ubuntu 22.04 LTS x86_64 (clean system).
- Public IPv4 (preferably also IPv6).
- Resources: 1 vCPU, 1–2 GB RAM, SSD from 20 GB (minimum).
Environment variables
YOUR_HOSTNAME— server FQDN, for examplebox.YOUR_DOMAIN.YOUR_DOMAIN— primary domain, for exampleexample.com.PUBLIC_IP,PUBLIC_IPV6— external addresses.ADMIN_EMAIL— initial admin account, for exampleadmin@YOUR_DOMAIN.TIMEZONE— time zone, for exampleEurope/Kyiv.
Basic OS preparation
Run the following sequence of commands. This will update the system and set the time zone.
sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -y upgrade
sudo timedatectl set-timezone Europe/Kyiv
# optional — set the hostname in advance, MIAB will take it as PRIMARY_HOSTNAME
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname YOUR_HOSTNAME
Tip: you can set the hostname in advance; MIAB will take it as PRIMARY_HOSTNAME.
Network security and ports
Open only the ports required for mail, web interface, and DNS. After applying the rules, verify from outside that they are in effect.
sudo ufw allow 25,53,80,110,143,443,465,587,993,995,4190/tcp
sudo ufw allow 53/udp
sudo ufw reload
sudo ufw status numbered
# first allow already established connections
sudo iptables -A INPUT -m conntrack --ctstate ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT
# then open the required TCP ports
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp -m multiport --dports 25,80,110,143,443,465,587,993,995,4190,53 -j ACCEPT
# and UDP for DNS
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p udp --dport 53 -j ACCEPT
# save the rules if needed (for example, via netfilter-persistent)
DNS preparation at the registrar
Choose one of the delegation scenarios. This determines further configuration and operation of the service.
Scenario A. MIAB as authoritative DNS (recommended for simplicity):
Create A/AAAA records for the subdomain box.YOUR_DOMAIN pointing to PUBLIC_IP/PUBLIC_IPV6, assign the following NS to the subdomain:
-
ns1.box.YOUR_DOMAIN -
ns2.box.YOUR_DOMAIN
If required by the registrar, add glue records for ns1 and ns2.
Scenario B. External DNS:
After installation, transfer all records that MIAB suggests to the DNS panel of your current registrar.
PTR/rDNS
Configure PTR (rDNS) to box.YOUR_DOMAIN. Without correct rDNS your sending reputation may drop and deliveries may be rejected.
Installing Mail-in-a-Box
Service conflicts
Important: before installing MAIB make sure no third-party MTA/DNS/Nginx/HTTP services are running on the server. MIAB will install the necessary components by itself.
Run the installation script. It will check OS compatibility, download the current version, and perform the deployment.
curl -s https://mailinabox.email/setup.sh | sudo bash
Key installer prompts
Provide the parameter values. They determine certificate issuance, DNS correctness, and mail reputation.
- PRIMARY_HOSTNAME:
box.YOUR_DOMAIN
PUBLIC_IP/PUBLIC_IPV6: leave auto detection if correct- ADMIN_EMAIL:
admin@YOUR_DOMAIN
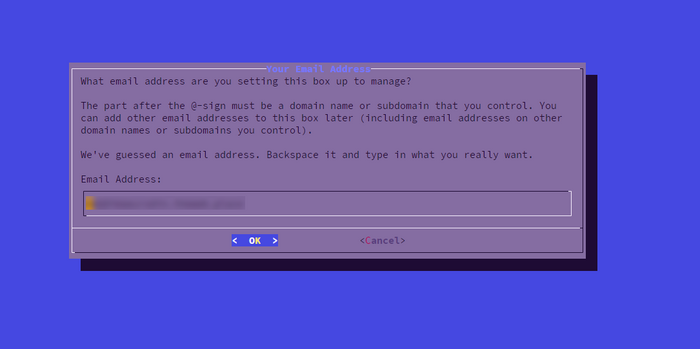
- Password for the admin panel: strong; save it in a password manager
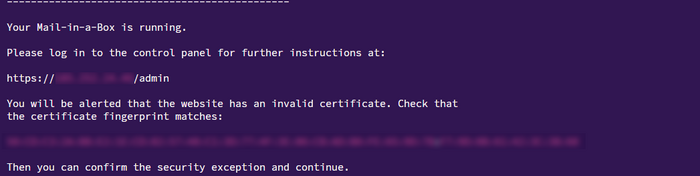
Note: Postfix, Dovecot, nsd (authoritative DNS), unbound (recursive resolver), Nginx, Fail2ban, Roundcube, Nextcloud (CalDAV/CardDAV), ActiveSync will be deployed, as well as Let’s Encrypt certificates issued and DKIM keys generated.
First login and status checks
Access to the admin panel
Open the panel URL and sign in using the administrator account created during installation.
https://box.YOUR_DOMAIN/admin
Status checks
In the admin panel open the System section, then the Status Checks tab. Resolve all warnings one by one until the status is green.
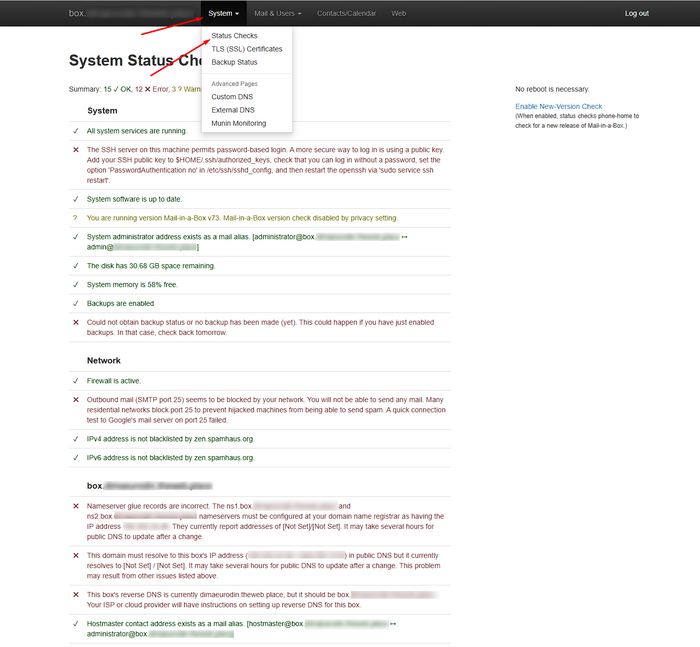
- When using external DNS, transfer A/AAAA, MX, TXT (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), CAA, SRV records to your registrar.
- Check port availability from outside, correctness of A/AAAA for
box.YOUR_DOMAIN, and presence of PTR. - If ports 80/443 were closed during installation, reissue certificates after opening the ports.
Noninteractive installation (automation/CI)
Use environment variables. This allows default deployment without dialogs.
export NONINTERACTIVE=1
export PUBLIC_IP=auto
export PUBLIC_IPV6=auto
export PRIMARY_HOSTNAME=box.YOUR_DOMAIN
# optional:
# export STORAGE_ROOT=/home/user-data
# export STORAGE_USER=user-data
curl -s https://mailinabox.email/setup.sh | sudo bash
The NONINTERACTIVE=1 variable enables noninteractive mode; the remaining parameters will be taken from the environment or determined automatically.
Verification and testing
Basic checks from the server
Run the commands to confirm service states and DNS record correctness. This helps detect issues before going live.
# distribution version
lsb_release -ds || cat /etc/os-release
# MIAB text menu (product version in the header)
sudo mailinabox
# status of key services
systemctl --no-pager --type=service | egrep 'postfix|dovecot|nginx|fail2ban|nsd|unbound'
# check mail TCP ports
nc -vz box.`YOUR_DOMAIN` 587
nc -vz box.`YOUR_DOMAIN` 993
# check critical DNS records
dig +short txt _dmarc.`YOUR_DOMAIN`
dig +short mx `YOUR_DOMAIN`
Expected result: all core services are active (running), MX points to box.YOUR_DOMAIN, correct TXT records for SPF/DKIM/DMARC are present.
Sending and receiving mail test
Perform an end-to-end messaging test to ensure correct authentication and delivery.
- Open webmail at
https://box.YOUR_DOMAIN/mail/. - Send a message to an external mailbox and check the headers: expected
SPF=pass,DKIM=pass,DMARC=pass. - Reply from the external mailbox to your domain and confirm receipt in Inbox.
| Symptom | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Certificates not issued | Ports 80/443 are blocked by an external firewall | Open the ports and in the panel initiate certificate renewal |
| DKIM/DMARC not validated | With external DNS, suggested records were not transferred | Transfer the records and wait for TTL to apply |
| Messages go to spam | No PTR or low reputation of the outgoing IP | Set rDNS to box.YOUR_DOMAIN, check RBL lists |
| No connection to IMAP/SMTP | Ports are blocked by provider/hoster | Open 587/993; clarify the policy regarding port 25 |
Additional configuration
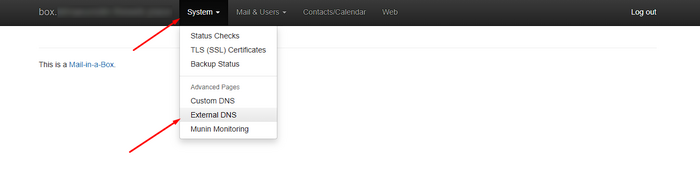
Using external DNS
In the admin panel open System, then External DNS. Enable external DNS mode and transfer A/AAAA, MX, TXT (SPF/DKIM/DMARC), CAA, SRV records to your current registrar. Note that applying changes may take up to 24 hours due to TTL.
Backups to S3-compatible storage and via SSH
In the admin panel open System, then Backups. Provide the provider parameters and run a write test, then a restore test.
S3_ENDPOINT=<endpoint>
S3_BUCKET=<bucket>
S3_ACCESS_KEY=<access_key>
S3_SECRET_KEY=<secret_key>
For SSH/SFTP, specify the host, port, and destination path according to your backup policy.
DMARC policy and report handling
Start with a relaxed policy p=none, collect and analyze aggregate reports, then tighten to quarantine or reject to improve resilience against domain spoofing.
v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; sp=quarantine; rua=mailto:dmarc@EXAMPLE.COM; ruf=mailto:dmarc@EXAMPLE.COM; adkim=s; aspf=s; fo=1
Logging and Fail2ban
Check active Fail2ban “jails” and review the logs of the main services for the current day. This helps quickly detect invalid authentication attempts and network anomalies.
sudo fail2ban-client status
sudo journalctl -u postfix -u dovecot -u nginx --since 'today'
It is recommended to integrate external monitoring and admin mail filters for prompt notifications.
Troubleshooting
Commands for quick analysis
-
Mail:
journalctl -u postfix -u dovecot -e -
Web:
tail -n 200 /var/log/nginx/error.log -
DNS:
journalctl -u nsd -u unbound -e -
Mail queue:
postqueue -p(remove stuck items:postsuper -d ALL)
Below are frequent symptoms with causes, actions, and entry points for diagnostics.
| Error / symptom | Cause | Solution | Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 550 Relay denied | Incorrect client SMTP authentication | Check login/password, use port 465/587 and STARTTLS | Review Postfix logs and client logs |
| TLS handshake failed | Unsynchronized time or incomplete certificate chain | Synchronize time and reissue the certificate | Run timedatectl, then in the panel open “System” and the “TLS” tab |
| SERVFAIL in DNS | Incorrect NS or missing glue records | Check NS at the registrar, ensure A/AAAA exist for ns1/ns2 |
Run dig NS YOUR_DOMAIN +trace |
| DKIM=neutral | Expired key or missing TXT record | Regenerate DKIM and update the TXT | In the panel open “Mail,” the “DNS” tab; additionally dig txt mail._domainkey.YOUR_DOMAIN |
Useful links and materials
Official documentation
- Official site: https://mailinabox.email/
- Repository: https://github.com/mail-in-a-box/mailinabox
- Issue tracker: https://github.com/mail-in-a-box/mailinabox/issues
- Specifications: DMARC (RFC 7489), DKIM (RFC 6376)