6.2.2 Basic Administration of Cloud VPS/VDS

You have accessed and successfully logged into the VM-Cloud control panel. How to use the control panel for basic tasks: monitoring, rebooting, and viewing server information? In this guide, we will explore how to perform basic administration and monitor the parameters of your servers.
Purpose of the Virtual Servers Tab
Most of the administration tasks for your Cloud VPS/VDS are performed within the Virtual Servers tab. Here, you have access to a wide range of information about the status of your servers and an extensive list of functionalities for managing them. The interface of this tab looks as follows:
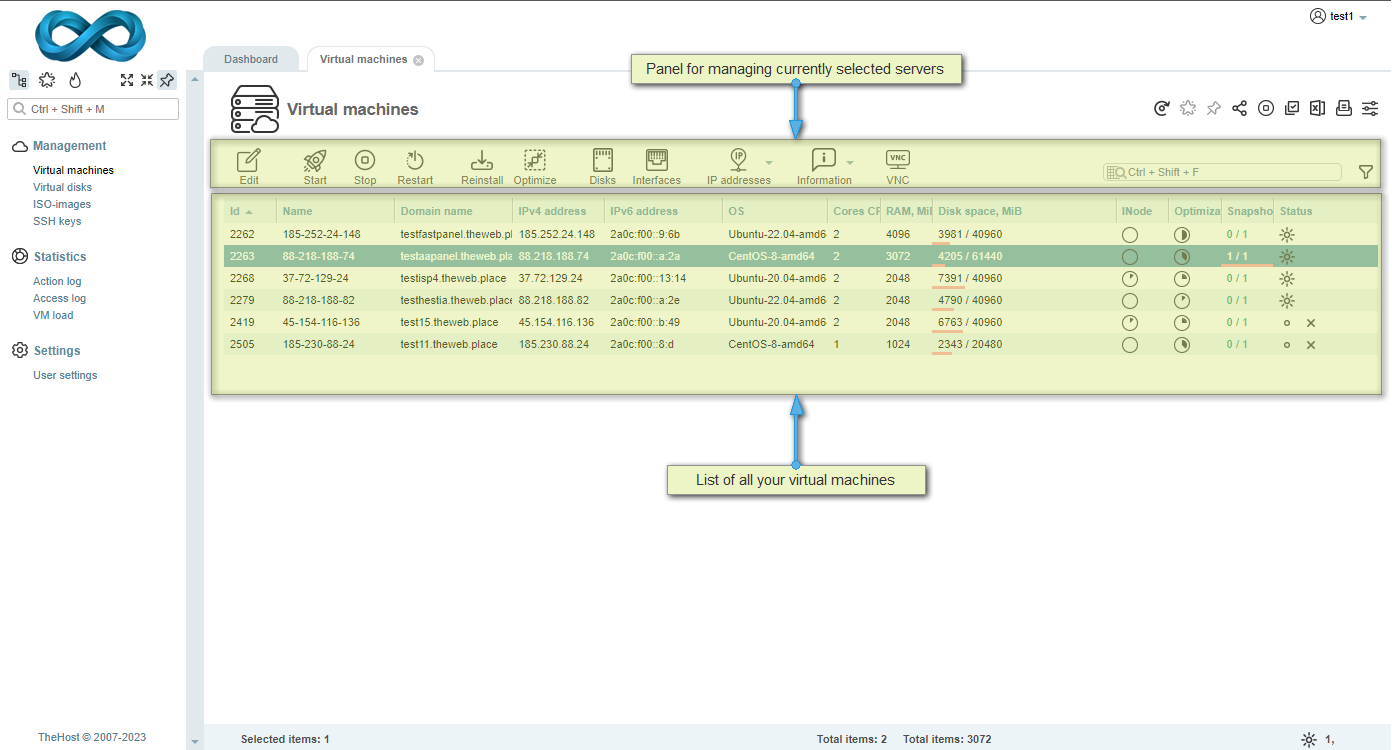
Additionaly: What information are displayed in your list of virtual machines:
- Id - the unique identifier of the server. It is technical in nature and cannot be changed.
- Name - identical to the primary IP of your server. Like the Id, it cannot be altered.
- Domain name - the actual name of your server, which you can change by clicking Edit. This will also change the PTR record for the server’s primary IP address.
- IPv4 address - the primary IPv4 address of your server. Additional addresses can be found in the IP addresses tab.
- IPv6 address - the primary IPv6 address of your server. Additional addresses can be found in the IP addresses tab.
- OS - the name of the OS installed on the server. The name may differ from the actual OS installed on the server if you specified a different name during the OS reinstall.
- Cores CPU - the number of allocated CPU cores. This depends on your package plan and any additional cores ordered in the configuration.
- RAM, MiB - the amount of RAM allocated to the machine in megabytes. This depends on your package plan and any additional RAM ordered in the configuration.
- Disk Space, MiB - the maximum and used disk space of your server. This depends on your package plan and any additional disk space ordered in the configuration. This information may be approximate; for greater accuracy, disk space should be checked using SSH or built-in OS tools.
- INode - the percentage of used INodes out of the allocated amount. The maximum is directly related to the amount of allocated disk space for the server. Relevant for UNIX systems.
- Optimization - indicates the current potential to optimize the server’s disk space usage. The optimization process can be initiated by clicking Optimize.
- Snapshots - the number of existing snapshots and the maximum number allowed for the server. We provide one free snapshot for any Cloud VPS/VDS pricing plan.
- Status - displays an icon indicating the current server status.
To perform any action on a server, you need to select it with your mouse and click the corresponding icon in the control panel.

Details: Functionality of each button in the control panel
- Edit – opens the editing form for the virtual machine.
- Start – powers on a shut-down server.
- Stop – shuts down an active server.
- Restart – performs a “hard” reboot of the server.
Note: A hard reboot will restart the server without a proper shutdown of its processes and may result in data loss. Unless absolutely necessary, it is better to reboot the server using the standard OS method.
- Reinstall - allows you to select the desired OS recipe and initiate its installation on the server. More details about this process are described here.
Important: Reinstalling the OS will completely erase all data on the server!
- Optimize - initiates the optimization of disk space usage on the server.
- Disks - displays a list of virtual disks connected to the VM. In this tab, you can also attach a new disk to the server, such as your ISO or GParted image. More details about this process are described here.
- Interfaces - lists the network interfaces of the server.
- IP addresses - opens a list of IP addresses assigned to the server, where you can also modify the PTR record for a specific IP address.
- Domains and NS- functionality for linking domains to TheHost’s NS. More details about this process are described here.
- Snapshots - opens the snapshot management form for the virtual server. More details on managing backups are described here.
- Backups - opens the backup management form for the virtual server. More details on managing backups are described here.
- Information - detailed information about the selected virtual server.
- Load - generates a report on the load for the specified VM.
- Bandwidth - generates a report on channel usage for the specified VM.
- Refresh Statistics - allows you to update the statistical information about the selected VM, which is displayed in the Virtual Servers tab.
- VNC - opens a VNC remote access terminal. More details on using VNC are described here.
Purpose of the Virtual Disks Tab
The Virtual Disks tab allows you to monitor the status of all disks active on your Cloud VPS/VDS. The interface of the tab looks as follows:
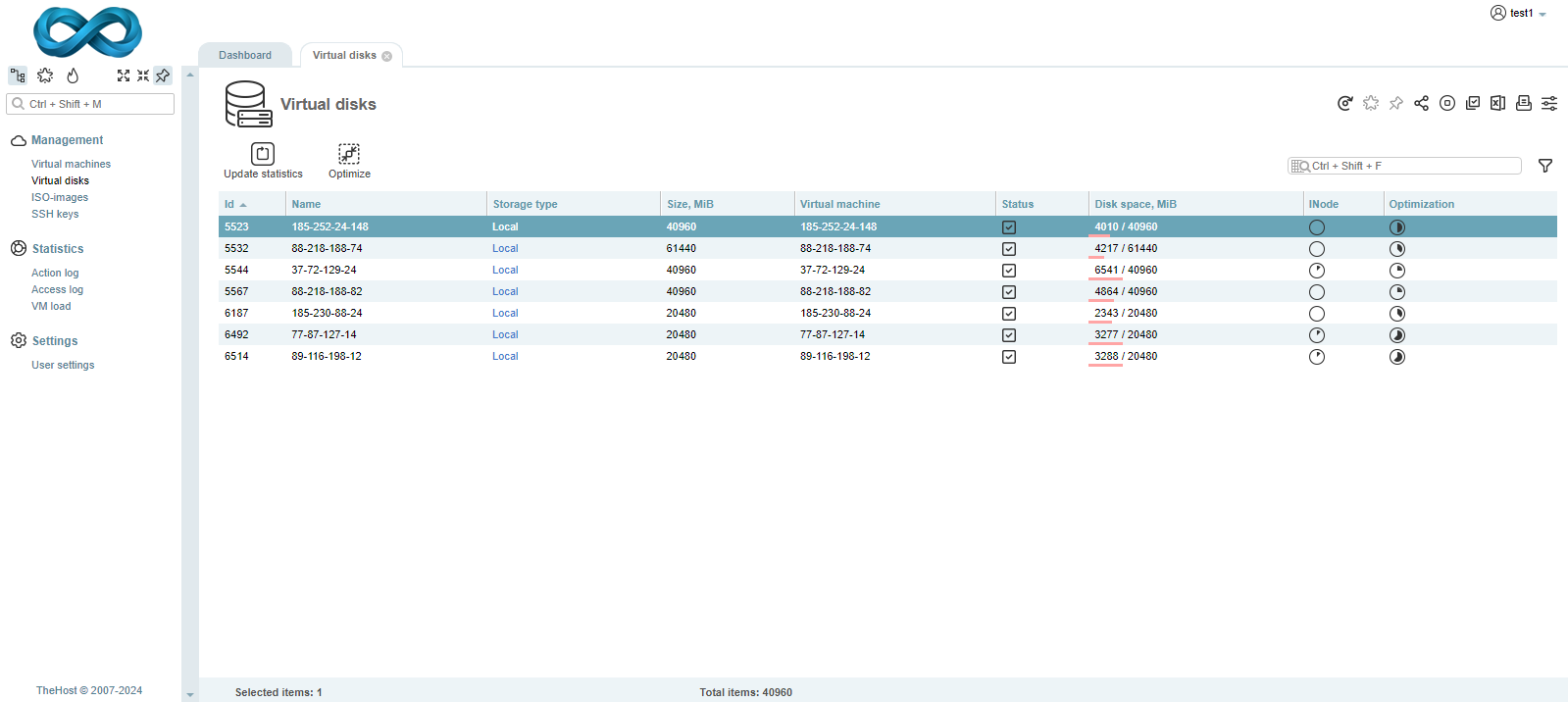
In addition to displaying information about the maximum size, free disk space, and INode, the tab also shows information about the potential for optimizing the actual disk usage by your server.
When the Optimization value reaches above 50%, we reccomend you initiate the optimization process of the virtual disk usage by clicking the Optimize button.
The described functionality in the Virtual Servers and Virtual Disks tabs allows you to perform any basic administrative tasks for your server. More complex tasks, such as reinstalling the OS or using VNC, are described in other instructions within this section of our Wiki.