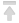6.1.1 How to Connect to Windows Remote Desktop

Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a protocol developed by Microsoft that allows users to connect to and manage remote computers over a network. It is widely used for remotely administering servers, providing technical support, and performing various tasks that require remote access to Windows desktops.
In practice, RDP allows you to use a remote computer almost as if it were your own. Using RDP, you minimize the requirements for computing power, disk size and, to some extent, the power consumption of your PC, placing all this on the remote computer.
In these relationships, the remote computer is often called the host, while your PC acts as the client.
Prerequisites
Based on the above, to connect you will need at least two machines: Host and Client. The requirements for them vary slightly.
Host
- Supported operating system. Windows Professional, Enterprise or Server. Windows Home does not have the built-in ability to become a host.
- Hardware requirements. Minimum system requirements to run the appropriate version of Windows.
- Network connection. Access to a local network or the Internet.
- System Settings: Activated the ability to accept incoming RDP connections in Windows settings.
Note: in the trial version of Windows Server, which we can install for our clients virtual and dedicated servers, all these requirements are met by default. Simply put, when you order these services from us, you immediately receive a host machine ready to work.
Warning: When installing the OC yourself, the ability to become an RDP host may be disabled by default. In this case, you will need to log into the server using VNC or IP-KVM and enable it.
Client
- Supported operating system. Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS or Android.
- Availability of a program for making an RDP connection. Starting with Windows XP, all Windows operating systems are equipped with the ability to connect via RDP as a default client.
- Network connection. Access to a local network or the Internet.
- Access parameters. To connect, the client needs to know the user name and password on the host computer. This user must also have the right to make an RDP connection.
Tip: You can always view the access parameters for your new servers using the Welcome button.
Question: My home PC does not run on Windows OS, what should I use to connect via RDP?
Examples of some popular clients, including official Microsoft clients for other operating systems:
- macOS: Microsoft Remote Desktop, CoRD, Royal TSX, Jump Desktop.
- Linux: Remmina, FreeRDP and rdesktop.
- iOS: Microsoft Remote Desktop Mobile, Jump Desktop, Parallels Access.
- Android: Microsoft Remote Desktop, aRDP, Remotix.
How to connect via RDP
Let’s look at an example of connecting from a client based on a client running Windows 10:
1. Click Start and search for the Remote Desktop Connection application. In modern versions of Windows, it can also be found using the abbreviation rdp.

Tip: If the Windows interface looks unusual, RDP can be called in alternative ways. For example, using the key combination Win+R and executing the mstsc command.
2. Open the application. The interface looks like this:

3. Click Show Options for an expanded view of the interface. Enter the IP address or hostname of the host machine in the Computer form, and the name of the user created on the server in the User name line.
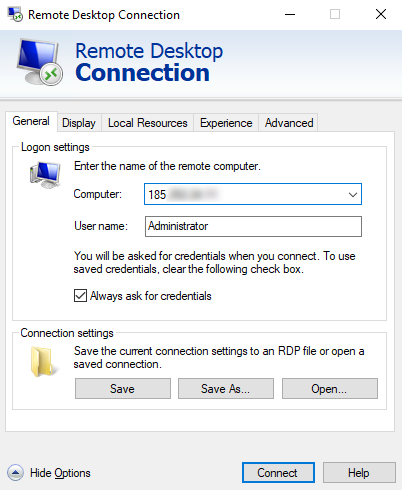
Important: when making the first connection to the host from your client, you will be required to accept a security certificate to establish the connection:
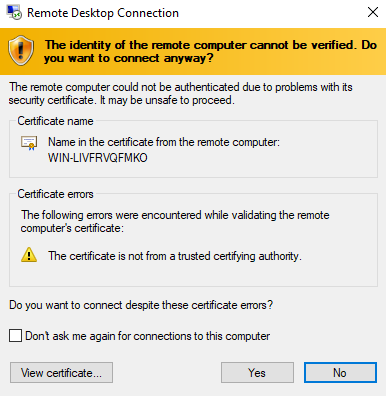
4. Click the Connect button. If the data is entered correctly, you will be prompted to enter the password for the previously specified user:
5. After entering the password, you will successfully connect via RDP.

Additional settings
In addition to making the connection itself, you can also configure some additional aspects of RDP in the program interface.
Using local resources on a remote computer
The most interesting possibility is the use of local resources of the client machine on the host machine.
To configure these parameters, you must go to the Local Resources tab before connecting.
In it you can configure the use of audio, microphone, printer, clipboard, keyboard shortcuts and, most importantly, the storage disks of the client machine on the host machine.
It’s very easy to do. In the Local devices and resources subsection, click the More details button. Then, simply mark the required disk with a checkmark:
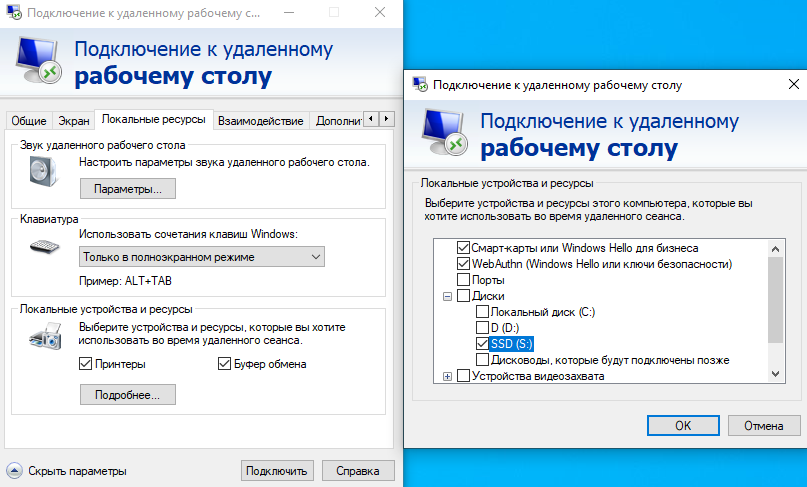
The next time you connect, your local disks will be available for use on the remote host without any restrictions.